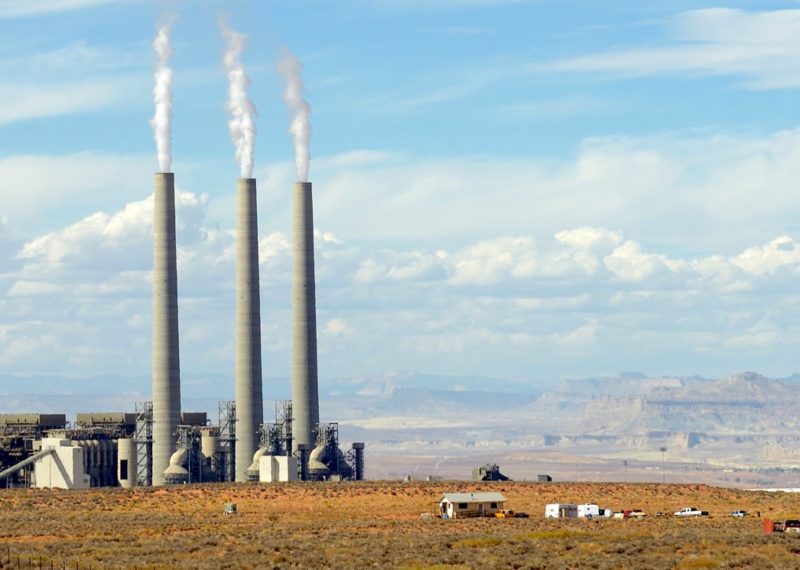
It looks like it doesn’t belong there. The lonely, aging power plant stands out against the red desert, connected to the nearest town by a single, crumbling road. It is an artifact, a relic from a time when coal was king.
Unless someone buys the Navajo Generating Station (NGS), it will go offline in 2019. The Arizona plant is struggling to compete with smaller, more nimble natural gas-fired generators, wind farms and solar arrays. Coal is simply too costly to compete. “You know the old saying, ‘You make money if you buy low and sell high’? They’re buying high and selling lower,” said David Schlissel, director of resource planning analysis at the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA).
If the Navajo Generating Station shuts down, locals will lose some 800 jobs, both at the plant and in the nearby Kayenta mine, which supplies coal to the generating station. Facing unemployment rates upwards of 40 percent, the Navajo and Hopi tribes are eager to protect those jobs, to say nothing of the revenue the operation provides.
“The Navajo Nation is so dependent on the jobs and the revenue for their budget. It’s really sad because, looking forward, it just doesn’t seem to be a sustainable economic enterprise,” Schlissel said. “I have no idea who would put their money here.”
Some, however, are happy to see the plant and the mine close down. While the operation is the cornerstone of the local economy, it is also a symbol of exploitation. Built on sacred land and without the consent of traditional leaders, the operation has better served its corporate owners than the tribes themselves. Thanks to a one-sided lease brokered by the federal government, for decades the Navajo and Hopi tribes received pennies on the dollar for every ton of coal mined.
Critics of the plant see its impending closure as an opportunity to create new businesses owned and operated by Native Americans in tourism, agriculture and energy. Experts believe the tribes could repurpose much of the existing energy infrastructure associated with the Navajo Generating Station to support new solar and wind projects. The transition to renewables would be difficult, but it could breathe life into the community.
In many ways, the embattled plant is a microcosm of a story unfolding across the country. As coal loses ground to natural gas and renewable energy, coal miners and plant operators are looking to the Trump administration to keep them afloat. But there is only so much that policymakers can do. The death of coal is not a matter of if, but when. In the coming years, coal communities will need to fight to stay alive. The Navajo Generating Station offers a preview of what’s to come.

The rise and fall of the Navajo Generating Station
The story of the Navajo Generating Station dates back to the late 19th century, when government surveyors discovered expansive reserves of copper on land inhabited by Hopis, Navajos and a handful of Mormon settlers. As Judith Nies explains in Unreal City, a history of coal power in the Southwest, President Chester A. Arthur worried that Mormons would snatch up the mineral-rich land at a time when demand for coal was on the rise.
In 1882, Thomas Edison flipped the switch on the world’s first commercial coal-fired power plant, and it was clear that the electrification of the United States would drive up demand for coal. That same year, Arthur signed an executive order creating an Indian reservation that spanned a large swath of Arizona coal deposits. The president’s order would keep coal reserves out of the hands of Mormon settlers, giving the federal government the opportunity to exploit those resources at a future date.
That day came nearly a century later, as the rapid growth of Los Angeles, Las Vegas and other cities in the Southwest spurred investments in coal power. In 1966, Navajo and Hopi leaders signed a lease allowing coal giant Peabody Energy to mine 40,000 of acres of their reservation. The lawyer who represented the Hopi tribe also represented Peabody, and he did much better for the coal company than he did for the Native Americans.
Nies writes that the Peabody lease “violated every guideline that the Department of Interior had set up for leasing on public lands: no competitive bidding, no automatic renegotiation clauses, a fixed rate rather than a percentage royalty rate.” At that time, the royalty rate on federal lands was $1.50 per ton of coal, but under the terms of the lease, the Hopi and Navajo tribes would earn just 37 cents on each ton of coal mined. Traditional Hopi leaders decried the lease as “arbitrary, capricious, an abuse of discretion.”

The deal was a giveaway to Peabody, but Nies writes the lease was “about more than money. It was about growth — the power to pump water into Phoenix, air-conditioning to Los Angeles, and the electricty to light the giant casinos and cool thousands of homes in Las Vegas as the population doubled and then tripled every year.” All of it depended on a steady supply of cheap electricty.
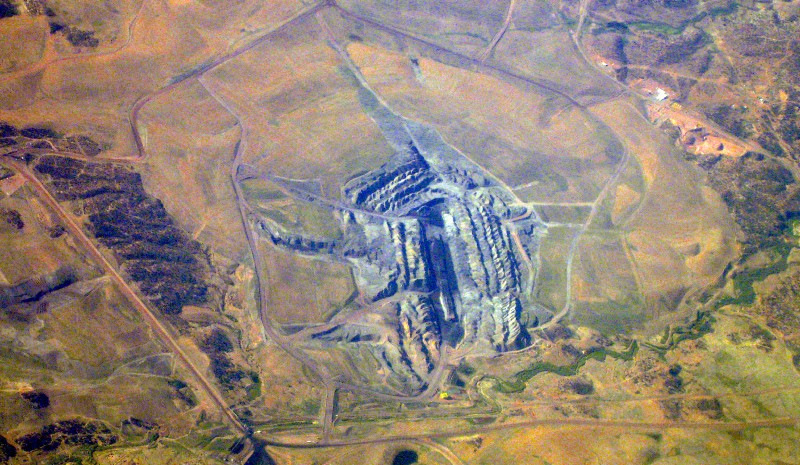
In 1973, Peabody began operations at the Kayenta mine. Three years later, the Navajo Generating Station came online, delivering power to customers across the Southwest. The tribe mined coal, exported electricity and imported money, but the biggest winners were Peabody energy and the power utilities that owned the plant. “The Navajo Nation really didn’t get its fair share out of those operations,” said Brett Isaac, a Navajo solar entrepreneur. “It tied us to those jobs and didn’t allow us to diversify.”
Now, with the plant set to close, workers are worried about how they will make ends meet. “A lot of the miners and plant operators, they are pretty much lifelong employees of that operation,” Isaac said. “I have an uncle who has worked at the Peabody mine since right out of high school. The next week after graduation he started working at the mine. He’s never had to apply for a job.”
Until recently, coal was the country’s cheapest and most abundant source of power, and utilities relied on large facilities like the Navajo Generating Station to provide a reliable stream of electricity. In recent years, however, coal has lost ground to other power sources. Wind and solar are growing cheaper by the day, while advances in hydraulic fracturing have made natural gas more affordable than coal. Small, gas-fired power plants can ramp up and down more quickly than large, coal plants, allowing them to track consumer demand more closely.
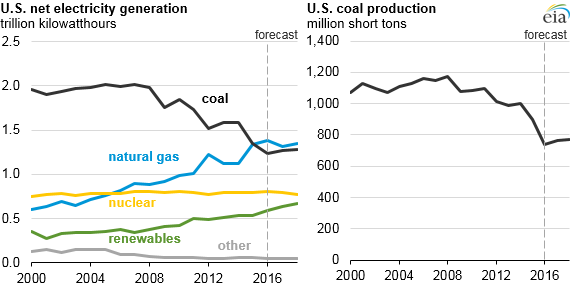
“The fact of the matter is all of the major utilities in the region, who are already co-owners of the plant, have decided for economic reasons that it’s cheaper for them to produce their own power or buy power from gas and renewables,” said Roger Clark, a program director at the Grand Canyon Trust, a conservation group based in Arizona.
“The outlook has gotten dimmer and dimmer as the years have past,” Isaac said. “We knew we would have to diversify, but we didn’t think it would be this sudden.”
The Navajo Generating Station is in an especially precarious position. Because the plant is situated 4,000 feet above sea-level, where the air is thinner, the coal burns less efficiently than it would at a lower elevation. The plant is also hundreds of miles away from major markets like Las Vegas and Los Angeles, and some electricity is inevitably lost en route. Utilities would rather generate power from solar, wind or natural gas closer to where it’s being used.
“For one thing, you’re not having to pay 800 people to run the mine and the power plant,” said Clark. At a gas-fired power plant, “a shift might be three to five people. At the Navajo Generating Station, it’s several hundred people.”
The high cost of generating coal power is only one dilemma. There is also the human cost of operating the mine — which has left a generation of workers with black lung — or the power plant — which is the seventh-largest source of carbon pollution in the United States, and a font of toxic chemicals that worsen asthma, provoke heart attacks and shorten lives. Pollution from the plant can be seen as far away as the Grand Canyon.
“You can see the haze,” said Isaac, who lamented the years of operation. “What did it actually cost us? People getting sick.”
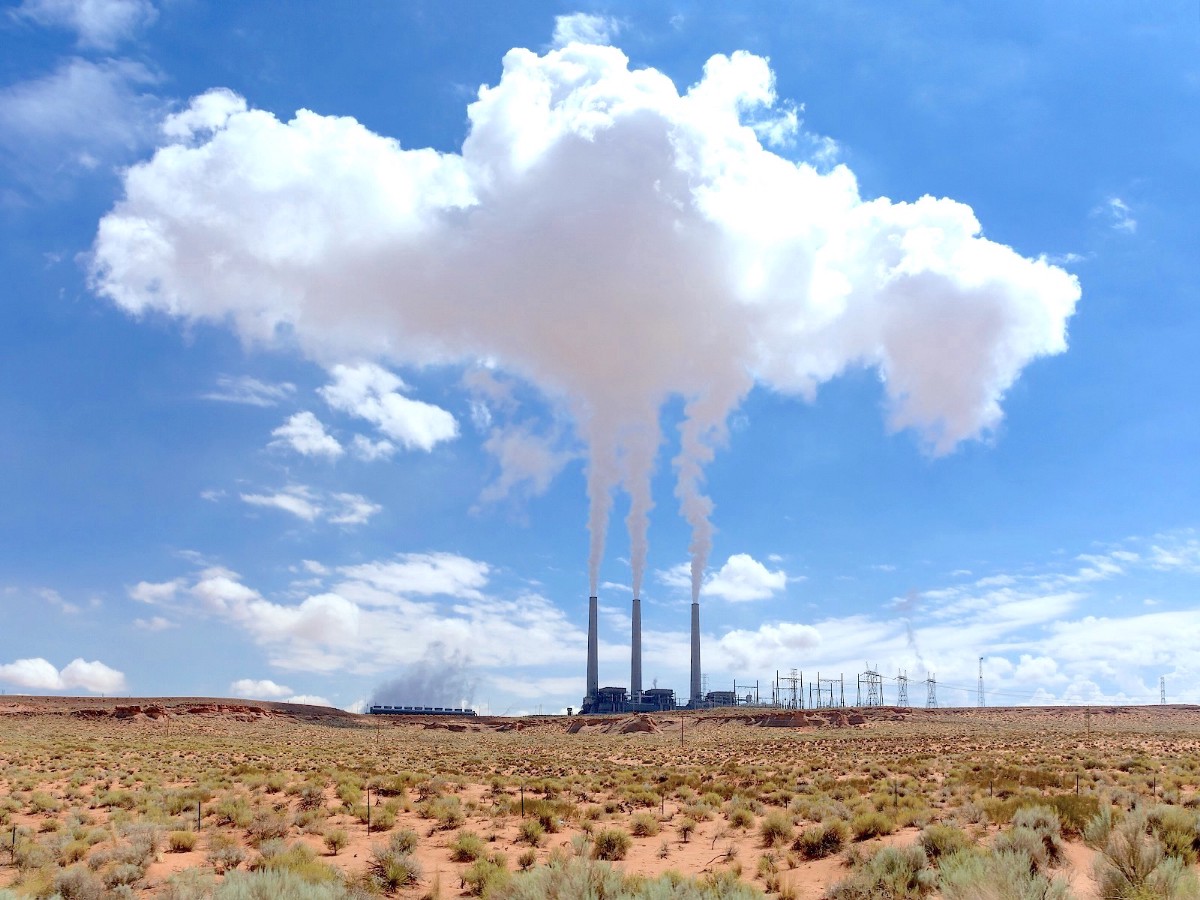

A power plant on life support
Perhaps more than the Hopi and Navajo tribes, Peabody is determined to keep the Navajo Generating Station open. The coal company said it has found a number of potential buyers for the plant, but it has not disclosed any names. It seems unlikely that investors would be lining up to purchase the generating station. IEEFA projects it would cost upwards of $400 million to keep the plan online through the end of 2019, and it could cost more than $2 billion in subsidies to keep the plant running through 2030.
Peabody has an ally in Trump administration, which is desperate to make good on its promise to rescue coal. In addition to rolling back dozens of environmental safeguards, the administration is pushing regulators to compel utilities to buy costly, polluting coal power. It has made the Navajo Generating Station a priority, not simply because the federal government has an ownership stake in the plant.
“If NGS closes, it will be very damaging for the administration,” Mike McKenna, who served on Trump’s transition team, told ClimateWire. “Closure is a preventable tragedy. The administration needs to prevent it.”
Representatives from Peabody Energy recently met with officials at the Department of the Interior and the Department of Energy, as did Navajo and Hopi leaders. Interior Secretary Ryan Zinke is exploring options for keeping the plant open, including erecting a high-powered solar facility that would be compatible with the current operation.
“Since the first weeks of the Trump administration, one of Interior’s top priorities has been to roll up our sleeves with diverse stakeholders in search of an economic path forward to extend NGS and Kayenta Mine operations after 2019,” Zinke said in a statement in June. The administration has yet to put forward a plan to stave off the plant’s closure.

An uncertain future for the Navajo and Hopi tribes
It’s unclear how locals could replace the jobs and revenue from the Navajo Generating Station, but experts have a few ideas. A recent report from IEEFA proposed that the Bureau of Reclamation, Peabody and the utilities who own the plant “provide a substantial core of replacement jobs that require skill sets similar to those of the existing workforce.”
The report also recommended the tribes invest in infrastructure, tourism, agriculture and water. Clark pointed to the infrastructure associated with the power plant, which includes a water pump, power lines and an electric railroad that runs from the mine to the generating station. “All of these things might be able to be repurposed into a renewable-energy powered water system,” he said.
The power plant uses as much as 30,000 acre-feet of water each year, water that is siphoned from Lake Powell using a large pump, Clark explained. “If the power plant is taken down, that pump is a stranded asset, which also might complement the fact that the Navajo Nation itself has a legitimate claim to every bit of that water that the power plant is using plus another 20,000 acre-feet,” he said.
The Navajo tribe could build solar arrays to power the pump, which could be used to carry water from Lake Powell to the current site of the plant, a high point in the region. Water could then be fed to other parts of the reservation. “The water itself may be worth more than the coal to the Navajo Nation,” Clark said.
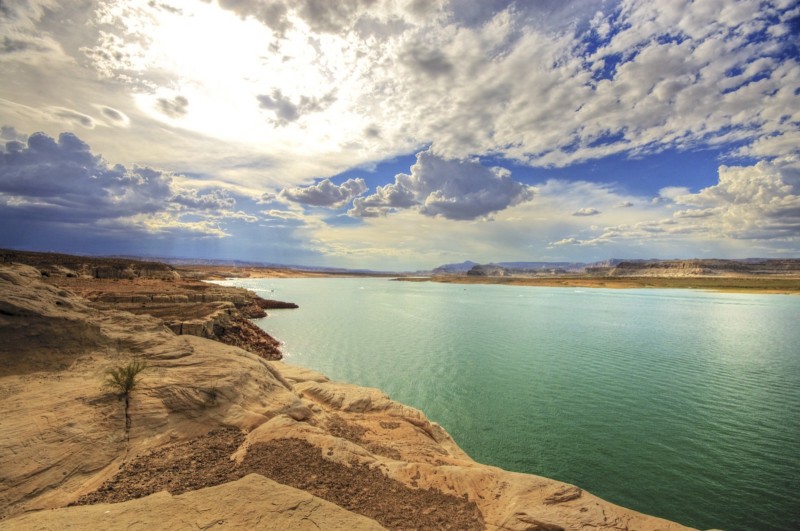

The Navajo tribe could also invest in clean energy, both to sell across state lines and to power locally. “Other states don’t buy coal power anymore,” Isaac said, “but other states will buy renewable energy. So, we’re looking for ways that we can capitalize on that.”
A 2012 report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that “neither solar, wind, nor geothermal power alone can replace all the types of benefits currently provided by [the Navajo Generating Station]. They might in aggregate, however.” The IEEFA report found that solar power could “replace some of the lost generation capacity, jobs and revenue” from the plant’s closure.
Isaac said that many Navajos doubt the viability of clean energy, so they built mobile solar power units to bring electricity to parts of the reservation that are off the grid — around a third of homes on the Navajo Reservation lack power. “I wanted to build something that people could touch,” Isaac said. “Essentially, we’re building stories, because that is hopefully what’s going to encourage communities to shift.”
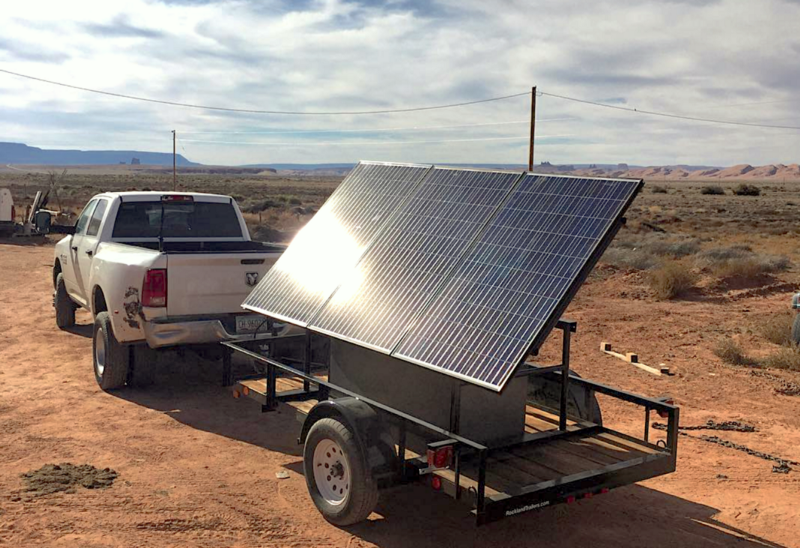

The Department of Commerce is awarding some $420,000 to the Navajo and Hopi tribes to help them cope with the plant’s closure, money that could be used to implement some of these ideas. Even if the plant stays online for a few more years, it is inevitable that it will close sooner rather than later. Any effort to keep the plant open distracts from the hard work of creating new businesses. Isaac says the Navajo tribe needs to look beyond coal for jobs and income.
“We seriously thought we couldn’t survive without that royalty. We couldn’t survive without those jobs. We kind of put ourselves in a corner when it came to how to discuss the economic impact,” Isaac said. “It’s going to hurt, but we are a lot more savvy than we give ourselves credit for.”
Jeremy Deaton writes for Nexus Media, a syndicated newswire covering climate, energy, policy, art and culture. You can follow him @deaton_jeremy.


